BioJava3 eclipse
Eclipse is a common IDE for using BioJava.
Prerequisites
- Download Eclipse from http://www.eclipse.org/. Several flavors are available, which come with different pre-installed plugins. We recommend starting with ‘Eclipse IDE for Java Developers’.
- Install the following plugins. See Plugin
Installation below for detailed
instructions.
- m2e - Maven Integration for Eclipse
- Eclipse EGit
- m2e-egit SCM Handler
Cloning the repository
We recommend creating a
fork on github for
day-to-day development. In the following instructions you should
substitute something like ‘https://github.com/
Option 1: Try these instructions first. If they don’t work, try option 2.
- Go to
- In the Maven category, select ‘Check out Maven Projects from SCM’ and click Next.
- Select ‘git’ in the dropdown box. If ‘git’ is not an option, make sure you have the m2e-egit connector installed as descripted below.
-
Add the URL for your biojava repository on github. For instance, to checkout the main repository, use https://github.com/biojava/biojava.git
Make sure that ‘Checkout All Projects’ is selected and click Finish. Eclipse will download the source code in the background, indicated by the progress bar in the lower right corner. After a few minutes the Package Explorer pane should populate with the BioJava submodules.
- Initiate git tracking for the projects
- Select all biojava modules in the Project Explorer
- Right click and select
- Select ‘Git’ and click Next
- Select ‘Use or create repository in parent folder of project’. This will make {Eclipse Workspace}/biojava into the local git repository.
Finished!
Option 2: These instructions are more difficult, but may work if Option 1 fails.
- Open the Git Repository View
- Go to
- Under ‘Git’, select ‘Git Repositories’
- Clone your git repository. The following is the easiest way to do
this from within Eclipse, but you could also get a local clone via
the command line and then add it as a local repository.
- Click the ‘Clone Git Repository’ icon in the Git Repository View
-
Add the URL of your biojava repository on github. For instance, to checkout the main repository, use https://github.com/biojava/biojava.git
- Optionally add your Github username and password, then click Next.
- Select which branches to include. If you plan to commit any changes, we recommend only tracking the ‘master’ branch, so you don’t accidentally initiate a release. If you want the last stable version, you can select ‘release’ instead. Click Next.
- Choose a destination directory (outside your Eclipse workspace), double-check your selection of Initial branch, and click Finish
- Import Maven projects from the git repository.
- Right click on the biojava git repository in the Git Repositories viewer. Select ‘Import Maven Projects…’
- Select all modules and click Finish. Eclipse will download the source code in the background, indicated by the progress bar in the lower right corner. After a few minutes the Package Explorer pane should populate with the BioJava submodules.
- Initiate git tracking for the projects
- Select all biojava modules in the Project Explorer
- Right click and select
- Select ‘Git’ and click Next
- Select ‘Use or create repository in parent folder of project’. This will use the local repository you cloned previously for your source code
- Finished!
Option 3: Cloning from command line and importing into eclipse, doesn’t require SCM handler.
-
Clone biojava from command line git clone https://github.com/biojava/biojava.git
- Go to
- Browse to the root directory of your cloned biojava project
- Click OK and then Finish
- You are done! now eclipse will automatically detect all the pom.xml files (the maven config files) and will understand that it is a maven and a git-tracked project.
You should now have source to all the biojava modules (/wiki/BioJava3-core, biojava3-structure, etc). Viewing the history for any file should show you all commits since 2009 which have contributed to that file.
Plugin Installation
This section needs to be expanded with specific instructions for installing plugins using either Marketplace or directly from the Install software menu.
Recent versions of Eclipse come with the Marketplace plugin, which can be used to find and install additional plugins. Feel free to install the prerequisites from Marketplace. This tutorial uses the older method of installing plugins directly from their repositories, which is compatible with more versions of Eclipse.
1. Install Maven m2e
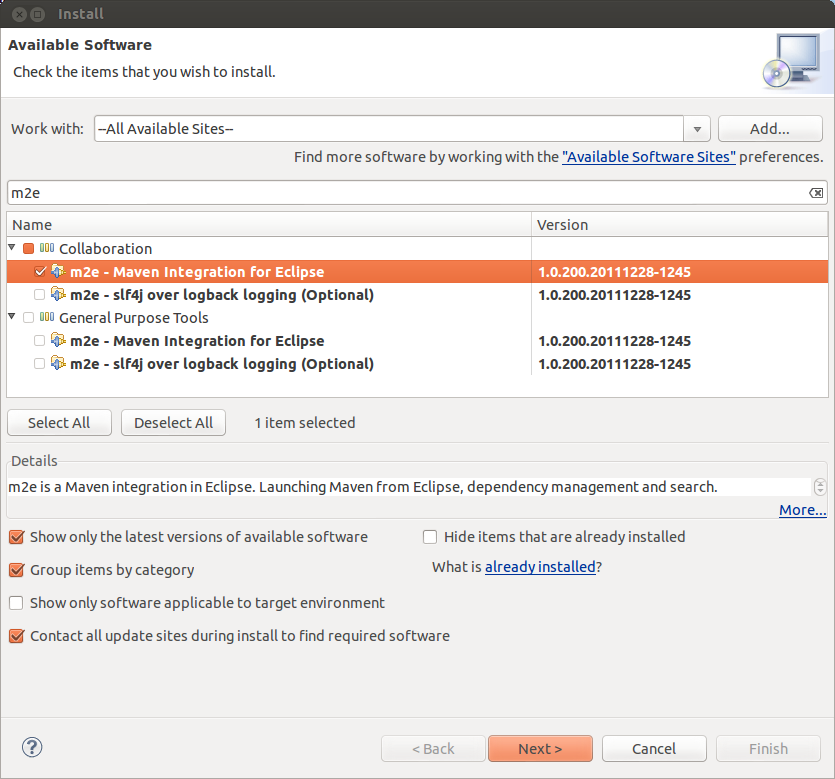
- In eclipse, go to
- Choose ‘–All Available Sites–’ from the ‘Work with’ dropdown
- Search for ‘m2e’ and check the box next to ‘m2e - Maven Integration for Eclipse’ under Collaboration
- Click ‘Next’, accept the license, and finish the installation
- Restart Eclipse at the prompt
If everything went smoothly, after reboot the ‘Welcome’ screen should mention ‘Maven Integration for Eclipse’.
2. Install EGit
Installing egit is very similar to installing m2e.
- In eclipse, go to
- Choose ‘–All Available Sites–’ from the ‘Work with’ dropdown
- Search for ‘egit’ and check the box next to ‘Eclipse EGit’ under Collaboration
- Click ‘Next’, accept the license, and finish the installation
- Restart Eclipse at the prompt
After rebooting, the Welcome screen should have a section about Git.
3. Install the SCM Handler
](EGit SCM install 1.png)
](EGit SCM install 2.png)
](EGit SCM install 3.png)
- Go to
- In the Maven category, select ‘Check out Maven Projects from SCM’ and click Next
- At this point, the Git connector is not installed, so the ‘SCM URL’ dropdown will either be blank or will only contain other SCM connectors like SVN. Click ‘Find more SCM connectors in the m2e Marketplace’
- Search for ‘egit’ in the ‘Install m2e connectors’ dialog. Check the ‘m2e-egit’ connector and click Finish.
- Click through the installer dialog and license. The security warning about unsigned content is safe to ignore.
- Restart eclipse (last time!)
Eclipse should now be ready to get the latest checkout of BioJava. See Cloning the repository above.
Configuring EGit
You should set your git name and email in Eclipse.
- Go to Eclipse Preferences
- View
- In the ‘User Settings’ tab, update your name and email.